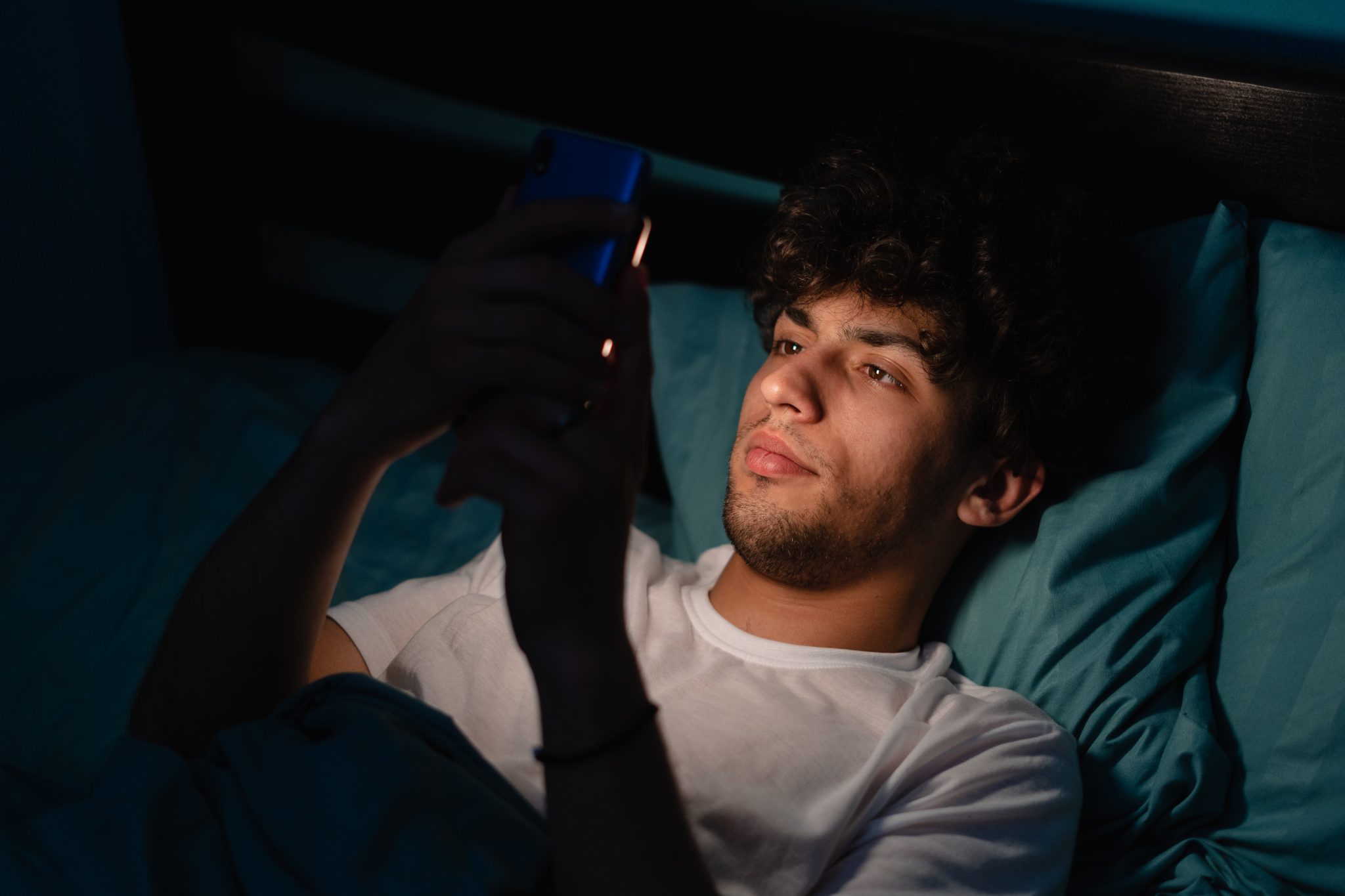

These days it seems that people of all ages are turning to chatbots to satisfy some of our most fundamental human needs, especially conversational interactions, friendship connections, and romantic courtships.
Those who regularly engage with chatbots may or may not realize that they may actually be forfeiting genuine connections in exchange for digital illusions.
Emerging research is sounding the alarm about the dangers of human-AI interaction.
AI companions, such as chatbots, have been programmed to provide emotional support. While this may sound fine on paper, such “pseudo-intimacy” often turns out to be a double-edged sword.
People are interacting with AI “personalities” that are programmed to be encouraging of whatever is being discussed. Responses to questions are instantaneous. They are also typically tailored to satisfy the human user’s personal desires.
A 2024 study in the Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication highlighted how algorithmic communications mimic closeness but also lack the authenticity of genuine human bonds. The resultant bi-directional interactions lead users to over-interpret superficial cues and form unhealthy dependencies.
Far from alleviating isolation, such interactions often deepen it as users retreat from the unpredictable nature of real relationships into the sterile comfort of contrived companionship.
AI-driven tools in the workplace automate collaboration, diminishing the need for human teamwork. This weakens human bonds.
Employees who frequently interact with AI systems report higher levels of loneliness, which in turn may be linked to insomnia and other potentially harmful post-work activity, such as excessive alcohol consumption.
People innately sense the artificiality of AI interaction. Recent surveys underscore this human response.
A Pew Research Center study from June 2025 found that a majority of Americans believe AI will worsen our ability to form meaningful relationships, with far more people seeing erosion rather than improvement in human connections.
As AI saturates our daily lives, instead of bridging gaps it appears to be widening them, prompting solitude to grow into a silent epidemic.
The digital age has already caused loss of empathy and erosion of essential social skills.
Human interaction thrives on in-person experience. An essential part of communication is non-verbal nuance. Speech and voice variations are accompanied by subtle glances, hesitant pauses, and empathetic nods.
In contrast, AI simplifies communication to digital prompts and programmed algorithms. Vital human elements are stripped away.
Research from the Gulu College of Health Sciences in March 2025 warns that excessive engagement with AI companions leads to decreased social skills, emotional detachment, and difficulties in maintaining authentic relationships.
By redefining communication norms, AI reduces our capacity for understanding non-verbal cues, which is a skill honed through face-to-face encounters.
Beyond the individual, AI-human interaction threatens the fabric of society. Algorithms curate echo chambers, limiting independent thought and fostering division.
As AI reshapes standards in communication and interaction, it blurs lines between human and machine, thereby normalizing friendless lives and eroding shared cultural and spiritual identities.
The resultant fragmentation from AI raises profound questions about consent, bias, and the commodification of intimacy. Without intervention, we face a world proliferated with AI relationships. It is a world fraught with danger to the well-being of both the individual and society at large.
A longitudinal study on chatbot use, published by MIT in March 2025, revealed rising concerns about its impact on real-world socialization. Overall, higher daily usage of chatbots correlated with higher loneliness and dependence.
Younger generations immersed in AI from childhood are particularly vulnerable, with studies showing reduced patience for ambiguity and a decline in social intelligence.
Social intelligence refers to an individual’s ability to comprehend, execute, and navigate social interaction, which, among other things, may include predominant verbal and non-verbal cues.
As users prioritize digital efficiency over interpersonal depth, society runs the risk of creating isolates, i.e., those who are proficient in prompting machines but inept at connecting with other individuals.
AI’s foray into mental health poses an additional alarming danger. Because access barriers to therapy are increasing, tens of thousands are turning to AI chatbots for mental health counseling.
A June 2025 Stanford study cautions that these mental health tools may reinforce stigma, deliver dangerous advice, or fall significantly short of human empathy.
Harvard researchers found similar results, also noting that emotional wellness apps foster serious attachments and dependencies and may potentially do more harm than good.
Increasing reports of AI-induced mental issues are mounting. Clinicians document cases of psychosis, suicide, and even murder-suicide, which are stemming from intense chatbot interactions.
It is not possible or, in my opinion, ethically acceptable to outsource the mental health needs of our people to a string of calculated algorithms.
Without boundaries, widespread use of non-human mental health counseling is resulting in atrophied social skills, increased loneliness, and, in the worst of cases, a collapse in mental health functioning.
Tech leaders have the responsibility to prioritize real connections over robotic replicas. It is essential for the AI industry to work towards more human-centric designs of technology.
It is also important to simultaneously implement a set of ethical standards. The underlying philosophy that defines the ethical standards will ultimately shape society’s destiny.
In my eyes, the future is binary. Each of us is being forced to make a decision.Take care in the choices that you make.
Humanity is hanging in the balance.





You must be logged in to post a comment.